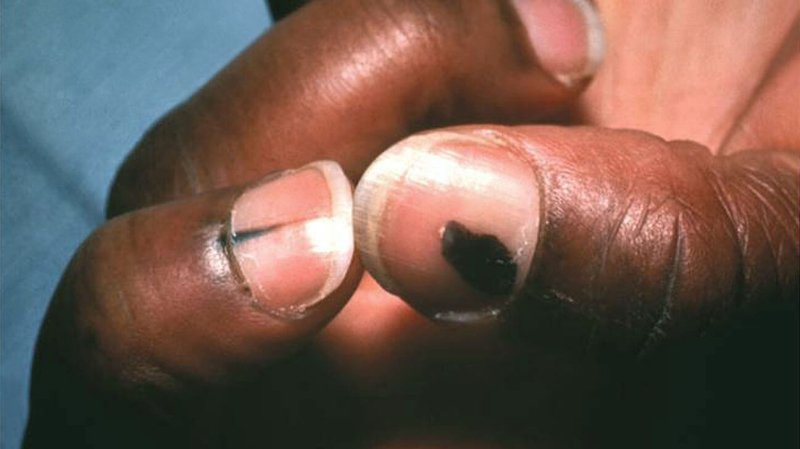
Historically, Black people and those with dark skin have been left out of efforts to combat skin cancer. Long neglected by sunscreen manufacturers and a medical community lagging in diversity and cultural competency — the acknowledgment of a patient’s heritage, beliefs, and values — many have not been informed about sun safety or how to check their skin for signs of damage or cancer.
To be sure, skin cancer rates are lower for people with dark skin tones. Melanoma is more than 20 times as common in white people as in African Americans, with an overall lifetime risk of 1 in 38 for white people compared with 1 in 1,000 for Black people. Melanin does provide some protection against sun damage, so those with more of it — those with darker skin — are better protected than those with fairer skin.
But overall, Black patients are more likely to be diagnosed with various forms of skin cancer at more advanced stages, said Dr. Janiene Luke, with the Skin of Color Society, a nonprofit that works to educate doctors and the public on skin health.
Given the known disparities in outcomes, Dr. Valerie Harvey, president of the Skin of Color Society, said two areas of research are needed: studying educational initiatives to see if awareness might lead to earlier diagnosis and improved survival; and determining risk factors in patients with dark skin, especially factors leading to the occurrence of melanoma in places less exposed to the sun.