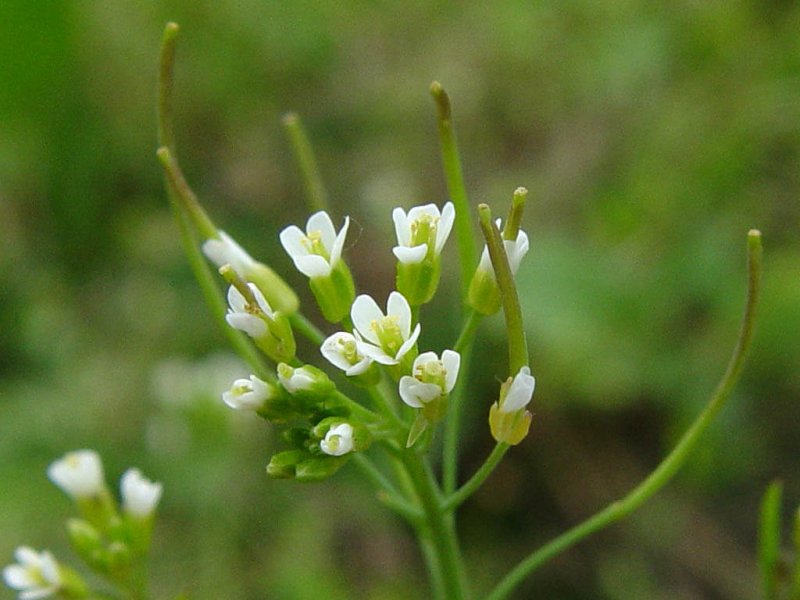
With a goal of breeding resilient crops that are better able to withstand drought and disease, University of California San Diego scientists have developed the first CRISPR-Cas9-based gene drive in plants.
While gene drive technology has been developed in insects to help stop the spread of vector-borne diseases such as malaria, researchers in Professor Yunde Zhao’s lab, along with colleagues at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, demonstrated the successful design of a CRISPR-Cas9-based gene drive that cuts and copies genetic elements in Arabidopsis plants.
Breaking from the traditional inheritance rules that dictate that offspring acquire genetic materials equally from each parent (Mendelian genetics), the new research uses CRISPR-Cas9 editing to transmit specific, targeted traits from a single parent in subsequent generations. Such genetic engineering could be used in agriculture to help plants defend against diseases to grow more productive crops. The technology also could help fortify plants against the impacts of climate change such as increased drought conditions in a warming world.