Since 1996, the global area planted to biotech crops has consistently increased, with significant expansion recorded in developing countries. In 2019, more than 17 million farmers from 29 countries planted 190.4 million hectares of biotech crops. Biotech crops are adopted globally and planted repeatedly by farmers because of their enormous benefits to the environment, human and animal health, and contributions to the improvement of socioeconomic conditions of farmers and the general public.
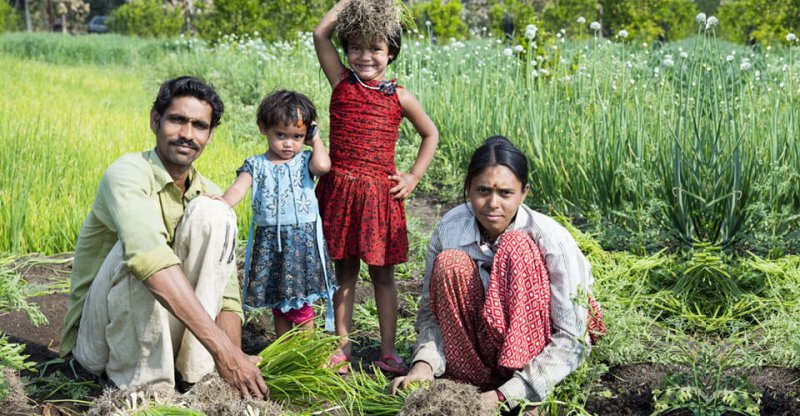
Through the years, biotech crops helped in increasing the income of small and resource-poor farmers, contributing directly to the poverty alleviation of a large majority (70%) of the world’s poorest people. Biotech crops have contributed to uplifting the economic situation of more than 17 million small farmers and their families totaling >65 million people, who are some of the poorest people in the world.
Farmers from different regions and countries planting biotech crops cite many benefits that they enjoy with planting biotech crops. These benefits include being able to pay for their children’s education, upgrading their farming equipment, reduced pesticide use, higher income, and having peace of mind.

Farmers from different regions and countries planting biotech crops cite many benefits that they enjoy with planting biotech crops. These benefits include being able to pay for their children’s education, upgrading their farming equipment, reduced pesticide use, higher income, and having peace of mind.
Biotech crops contribute to food, feed, and fiber security and self-sufficiency, including more affordable food, by increasing productivity and economic benefits sustainably at the farmer level. Biotech crops play an important role in increasing productivity per hectare and decreasing the cost of production as a result of the reduced need for inputs. From 1996 to 2018, crop productivity increased by 822 million tons valued at US$224.9 billion, and 86.9 million tons valued at US$18.9 billion in 2018 alone.
Biotech crops are a land-saving technology, capable of higher productivity on the current 1.5 billion hectares of arable land, and thereby help preclude deforestation and protect biodiversity in forests. Biotech crops helped conserve biodiversity from 1996 to 2018 by saving 231 million hectares of land and 24.3 million hectares of land in 2018 alone. Biotech crops also help provide a better environment by saving 776 million kg. a.i. of pesticides in 1996 to 2018 and by 51.7 million kg in 2018 alone from being released into the environment. Also in the same period, biotech crops helped save pesticide use by 8.3%, and by 8.6% in 2018 alone.

The important and urgent concerns about the environment have implications for biotech crops, which contribute to a reduction of greenhouse gases and help mitigate climate change. The combined permanent and additional savings through sequestration was equivalent to a saving of 23 billion kg of CO2 or removing 15.3 million cars off the road for one year.
Thus, biotech crops can contribute to a “sustainable intensification” strategy favored by many science academies worldwide, which allows productivity and production to be increased on the current 1.5 billion hectares only of global cropland, thereby saving forests and biodiversity. Biotech crops are essential but are not a panacea, and adherence to good farming practices such as rotations and resistance management, are a must for biotech crops as they are for conventional crops.