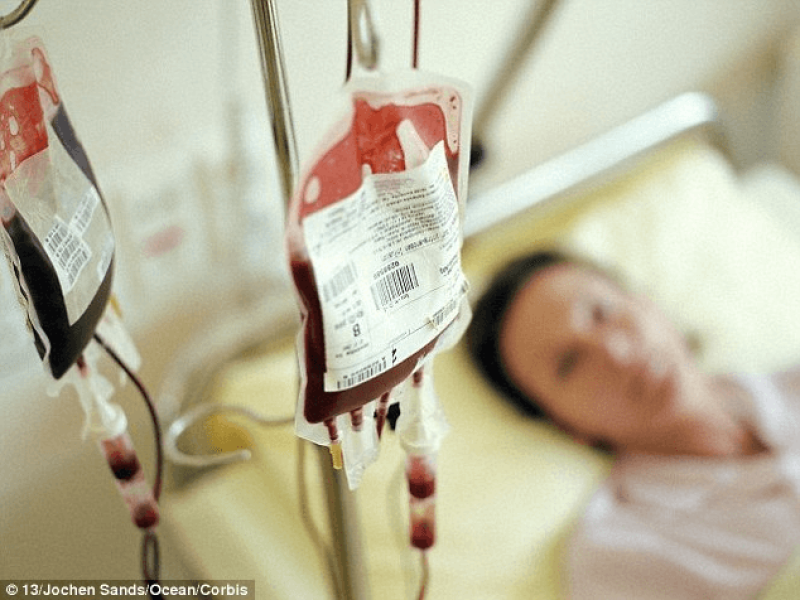
In a new study, patients will have their blood plasma completely replaced with plasma from young donors.
This will be the first time researchers test a total replacement of blood plasma. The study has recently started at Oslo University Hospital (OUS).
Maybe this could become a new treatment against Alzheimer’s disease.
In somewhat grim experiments, mice have been surgically joined to share circulatory systems. This led to unusual observations.
Older mice connected to younger mice appeared to reap benefits from the latter’s blood, whereas the younger mice seemed to deteriorate when exposed to the older mice’s blood.
…
In this recent study, patients are to receive blood plasma, which is the fluid component of blood and does not include the blood cells.
…
“We envision that the final treatment will not depend on donors. We aim to do analyses to find out exactly which molecules might have a beneficial effect and develop a treatment based on that,” [Oslo University Hospital researcher Petter Holland] says.
If the pilot study is successful, the plan is to start a larger study.