Most wireless sensors today communicate via embedded Bluetooth chips that are themselves powered by small batteries. But these conventional chips and power sources will likely be too bulky for next-generation sensors, which are taking on smaller, thinner, more flexible forms.
Now MIT engineers have devised a new kind of wearable sensor that communicates wirelessly without requiring onboard chips or batteries. Their design, detailed [August 18] in the journal Science, opens a path toward chip-free wireless sensors.
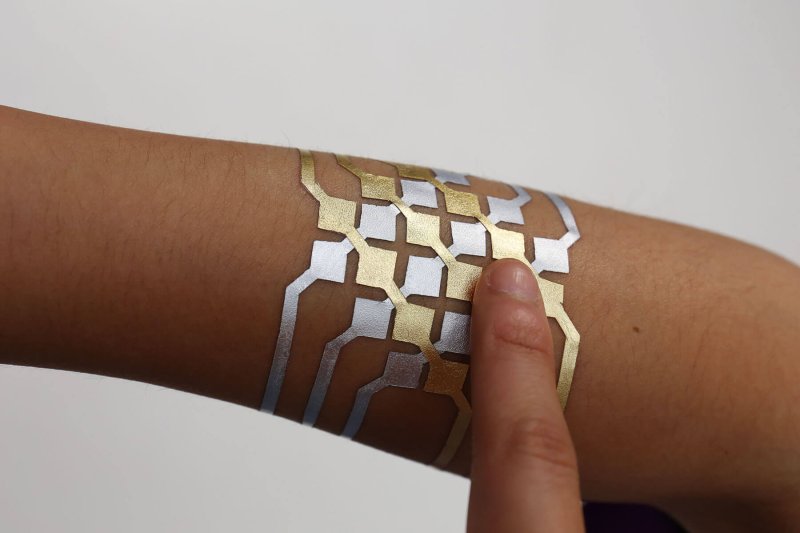
The team’s sensor design is a form of electronic skin, or “e-skin” — a flexible, semiconducting film that conforms to the skin like electronic Scotch tape.
“Chips require a lot of power, but our device could make a system very light without having any chips that are power-hungry,” says the study’s corresponding author, Jeehwan Kim, an associate professor of mechanical engineering and of materials science and engineering, and a principal investigator in the Research Laboratory of Electronics. “You could put it on your body like a bandage, and paired with a wireless reader on your cellphone, you could wirelessly monitor your pulse, sweat, and other biological signals.”