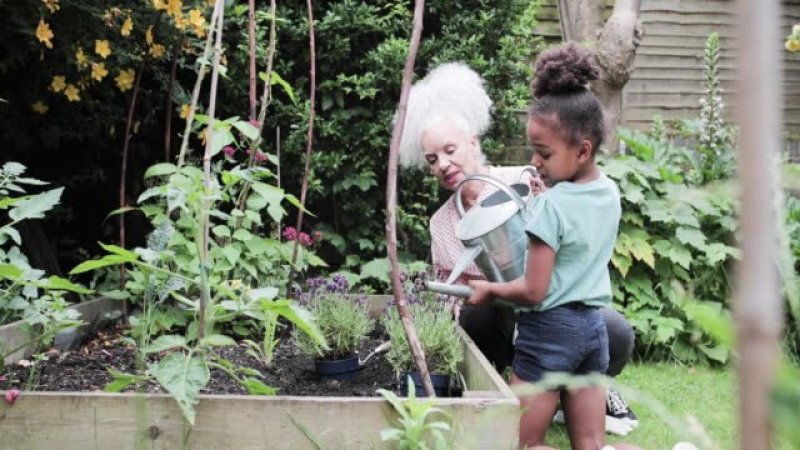
Hawkes found a correlation between how well children grew and their mother’s foraging work, until the mother had another kid. Then, their growth correlated with “grandmother’s work,” she says. “There were the data right in front of us.”
These observations, which Hawkes and collaborators began in the 1980s, have helped fuel the Grandmother Hypothesis, the idea that grandmothers step in to feed young children and perform other motherly duties so that mothers can focus their own energy and resources on having more children at shorter intervals. The result is that a grandmother enables the birth of more descendants, leaving more copies of her genes in subsequent generations.
Combining those observations with models of variation in life history in other organisms, from mice to elephants, Hawkes and colleagues have become convinced that human grandmothers have played a central role in the life history of Homo sapiens. They argue that grandmothers are a driving force behind the increased longevity of our species compared to other primates.