The Cenozoic is the name geologists give to the era spanning the last 66 million years, and it started with the mass extinction event that killed off (most of) the dinosaurs. There were incredible eruptions that contributed to the extinction event and spanned a considerable amount of time.
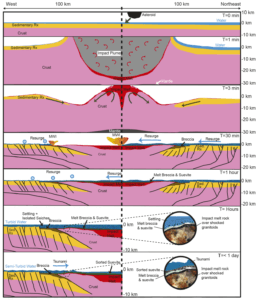
But the asteroid that struck off the coast of what is the Yucatán Peninsula today was the opposite—it couldn’t have been much more sudden. A recent drilling project recovered a long core of rock from the Chicxulub impact crater, leading to greater clarity about how the calamity played out—including on that first day.
…
While 30% to 50% of the rock struck by the Chicxulub impactor was made up of evaporite deposits like salt and gypsum, almost none of that material is found in the core. That provides more support for the idea that these minerals were vaporized, sending massive amounts of sulfur into the atmosphere where it could form sunlight-blocking particles. Much of the rest of the bedrock was limestone, which would have released CO2, causing the long-term global warming that followed after the short-lived sulfur particles washed out of the atmosphere.
Read full, original post: Here’s what happened in the impact crater the day it did in the dinos