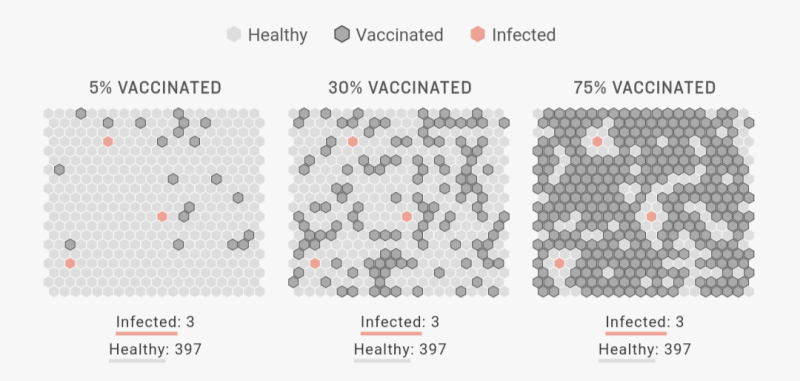
When you click “Run Simulation” [below], you are witnessing how a disease can spread through a population and how increased levels of vaccination can stop it in its tracks.
We’ve chosen to simulate a fake disease since there are too many unknowns to simulate the course of COVID-19. There are common features in how any infection spreads. When enough people are immune — through vaccination or natural immunity — a population achieves herd immunity. The disease stops spreading efficiently and starts to fade away.
One thing that’s evident from this simulation (and real life) is that the faster the population is protected by vaccination the better.