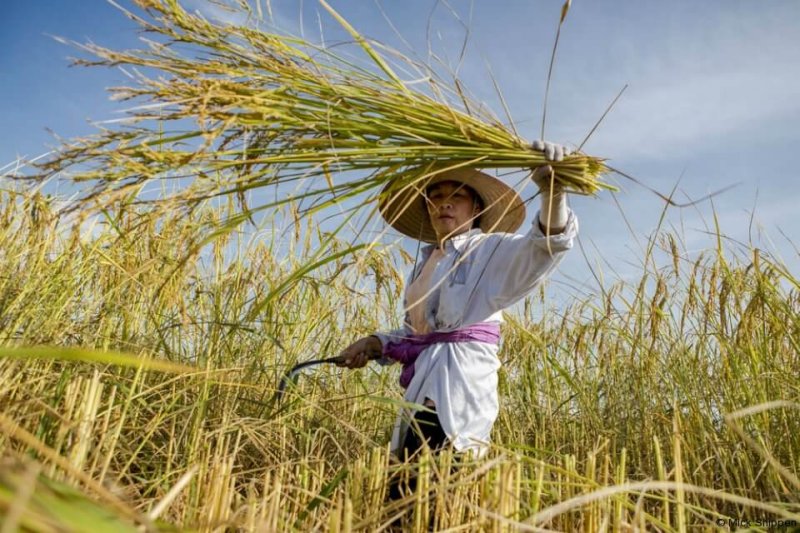
A team of scientists from Purdue University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences has used CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology to develop a variety of rice that produces 25-31 percent more grain and would have been virtually impossible to create through traditional breeding methods.
The team, led by Jian-Kang Zhu, a distinguished professor in the Department of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture at Purdue and director of the Shanghai Center for Plant Stress Biology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, made mutations to 13 genes associated with the phytohormone abscisic acid, known to play roles in plant stress tolerance and suppression of growth. Of several varieties created, one produced a plant that had little change in stress tolerance but produced 25 percent more grain in a field test in Shanghai, China, and 31 percent more in a field test conducted on China’s Hainan Island.
Their findings were published early online today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
…
“You couldn’t do targeted mutations like that with traditional plant breeding. You’d do random mutations and try to screen out the ones you don’t want,” [Purdue’s Ray A. Bressan] said. “It would have taken millions of plants. Basically, it’s not feasible. This is a real accomplishment that could not have been done without CRISPR.”
Read full, original post: CRISPR-edited rice plants produce major boost in grain yield