Daily Human Digest
Environment, genes equally at play in autism
Environmental factors are more important than previously thought in leading to autism, as big a factor as genes, according to ...

Nicholas Wade on race: Genes and evolution trump culture in shaping human differences
No subject is more taboo than race. New York Times science writer Nicholas Wade takes on the nature-nurture debate in ...

Breeding heat-resistant livestock for a post-warming world: A worthy endeavor?
Evan Halper at the LA Times chronicles efforts to breed livestock that can endure a warming world ... but should ...
Pace of biomedical research not sustainable without funding changes
In the current issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), four distinguished scientists make an urgent ...
Leukemia type can be detected by the shape of DNA’s packaging in nucleus
When someone has leukaemia, differences in how their genome is folded up into the nucleus of their cells can reveal ...
Genetic and maternal factors play larger role in neonatal brain injuries, long blamed on lack of oxygen during birth
It was long assumed that brain injuries in newborns resulted from insufficient oxygen during labor or delivery. Distressed parents often ...
Antibiotic resistance biggest issue in developing world because of lack of regulation
By most standards, the increasing availability of life-saving antibiotics in the developing world is a good thing. But, around the ...
Genetic sequencing offers promise of individualized medicine, but at what cost?
Whole genome sequencing has officially entered the medical mainstream and kicked off an era of truly personalized medicine. California-based Illumina ...

Stem cells can cure severe heart disease? Study suggests early reports may be oversold
A slew of positive reports showing that stem cells could be used to address severe heart disease are in question ...
Insects pass infections to their progency through sperm and eggs
The green rice leafhopper is never alone. When a female’s egg and a male’s sperm fuse into a new cell, ...
Sperm from skin cells have potential for male infertility treatment
Around 7.5 percent of men in the U.S. visit a fertility doctor at some point in their life, according to ...
Genes of benefit for athletic training response identified
There has long been a debate among doctors, scientists and psychologists about whether nature or nurture is more important in ...
Genetics make some people more vulnerable to repetitive brain injury
Scientists studying head injuries have found something surprising: Genes may make some people more susceptible to concussion and trauma than ...
Ancient, inert parts of our genomes may be protective
At hundreds of spots in our DNA, there are ancient swaths that have remained puzzlingly unchanged over hundreds of millions ...
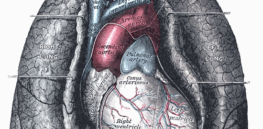
Genetically modified pig lungs or lab-grown lungs: Which is the future of our organ supply?
Biotech pioneer J. Craig Venter has aligned his company with efforts to create genetically modified lungs in pigs for human ...
Geography trumps genes in determining lifespan
Living in the Southeast is bad for your health. There is a huge range in the death rates across American ...

Sleeping sickness treatment in focus after sequencing of tsetse fly genome
Scientists have sequenced the tsetse fly's genome, Jennifer Frazer at National Geographic reports, revealing promising targets in the fight against ...
400,000 people entered into ancestory genetics database
The test analyzes a person’s genome at over 700,000 marker locations and provides customers with an easy and affordable way ...
Teeth of the very old may provide more easily accessible stem cells than blood
Normally, I wouldn’t post about a report that’s already reverberated through the blogosphere, but the finding of hundreds of mutations ...
Why don’t humans grow into Goliaths?
It’s no secret that a mouse stops growing before it becomes the size of a whale. But the physiological and ...
Protein in young blood fights aging
A protein in blood can repair age-related damage in the brains and muscles of old mice, returning them to a ...
Pig heart transplants successful in baboons, offer hope for human organ shortage
The unprecedented survival of pig hearts in four baboons for almost 600 days has revived hopes that animal organs could ...
Genetic primer course brought to you by New York Times
From junk DNA that, as it turns out, is not so junky after all, to the unique signatures in different ...
New job for IBM’s Watson: analyze cancer genetics to match patients with best available drugs
For years, the war on cancer has been about attacking specific body parts—developing treatment and funding research around lung cancer, ...
Camels carry MERS-causing virual DNA in their noses
Scientists have uncovered more evidence citing camels as the cause for the recent MERS-CoV virus outbreak sweeping across the Middle ...
Neanderthals not extinct from lack of smarts
Scientists have concluded that Neanderthals were not the primitive dimwits they are commonly portrayed to have been. The view of ...
HIV’s slow evolution in humans would not affect vaccine development
Scientists studying the evolution of HIV in North America have found evidence that the virus is slowly adapting over time ...

